今回はVue.jsとFlaskで手書き数字の認識を行って、結果の出力に合わせてCubismWeb(Live2D Cubism3SDK for Web)のモデルを動かしてみます。
アプリケーションのおおまかな動作
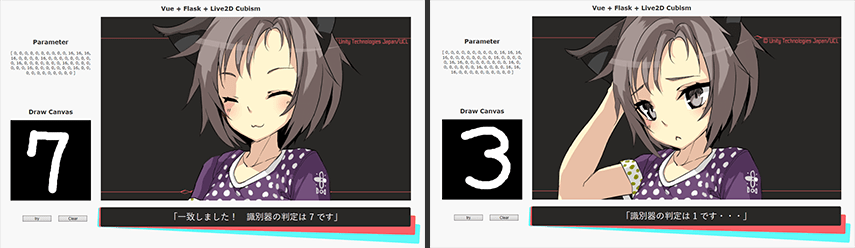
1. Vueのキャンバスにマウスで好きな数字を書く
2. キャンバスの内容を8×8に縮小して識別器に渡す
3. 識別器の判定結果をVueに返す
4. 判定結果を表示してCubismWebのモデルを更新する
5. ランダムで選ばれた数字(0~9)をキャンバスに書くことを依頼する
6. 依頼した数字と識別器の判定結果に応じてCubismWebのモデルを更新する
使用するイラスト
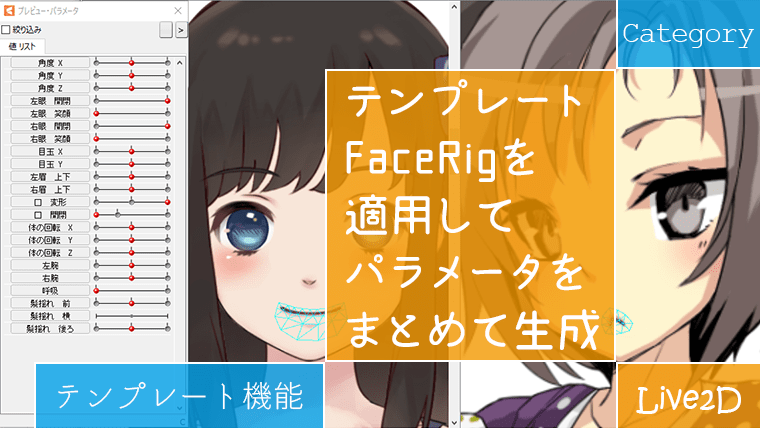
CubismWebで表示するモデルです。
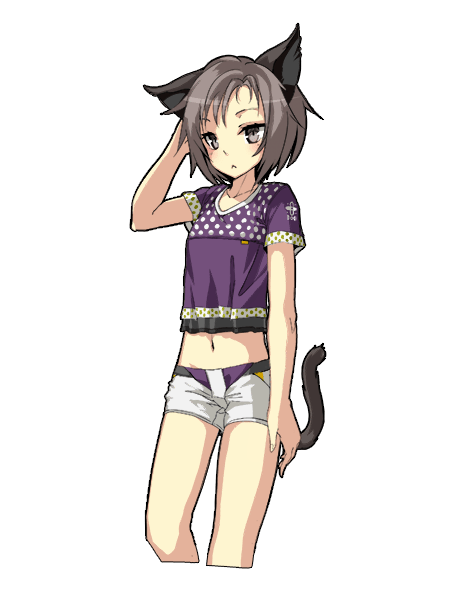
© Unity Technologies Japan/UCL
上記モデルには以前の記事で Live2D のテンプレート「FaceRig」を適用しています。
テンプレートを適用する手順についてはこちらで紹介しています。
動作確認サンプル
ChromeとEdgeで動作を確認しています。(下のサンプルはEdge)
Live2Dモデルで手書き数字の認識
Vue.jsとFlaskで認識した数字を、Live2Dモデル(CubismWeb)に渡すまでの過程を紹介します。
1. scikit-learnで手書き数字を学習させる
機械学習のライブラリ「scikit-learn」にはサンプルとしてデータセットが用意されているので、今回はその中から手書き数字の光学認識を学習させます。
前回記事「アヤメの分類」と同様にpickleファイルを識別器で使用します。
2. キャンバスを配置する
マウスで数字を書くためのキャンバスを配置します。
<div id="canvas_container"> <h2>Draw Canvas</h2> <canvas id="draw_canvas" width="280" height="280" @mousemove="drag_draw"></canvas> </div>

3. メッセージを表示するエリアとボタンの設置
判定結果などを表示するメッセージウィンドウを設置します。
<div id="message_window"> <p id="mes">[[ message ]]</p> </div>
キャンバスの値(0,255)を識別器に送るボタンと、キャンバスをリセットするボタンを設置します。
<div id="answer"> <button @click="getAnswer" id="btn">try</button> <button @click="clear">Clear</button> </div>
4. キャンバス関連の処理を記述する
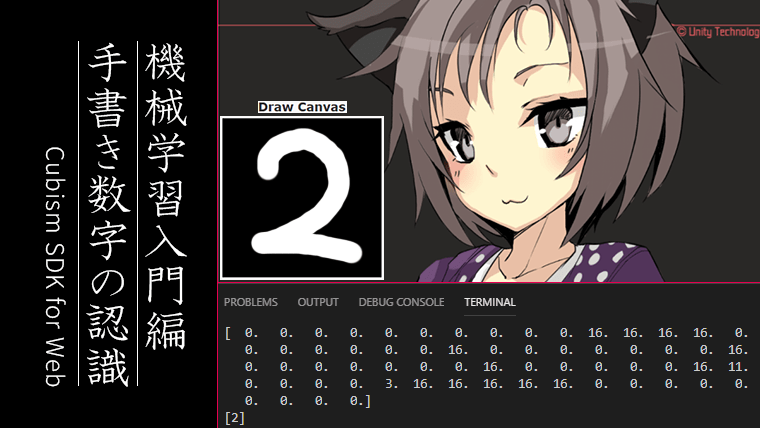
scikit-learnのサンプル(手書き数字)が8×8で書かれているので、それに合わせてキャンバスの内容も8×8に縮小して識別器に渡します。
識別器の精度を上げたい場合はMNISTなど別のデータセットで学習させた方が良さそうです。
<script>
const ans = new Vue({
el: "#exa",
delimiters: ["[[", "]]"],
data: {
message: '// 0~9の手書き数字を識別します //',
},
methods: {
update_message: function(str) {
this.message = str;
},
clear: function() {
const canvas = document.getElementById('draw_canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.fillStyle = 'black';
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
},
drag_draw: function(e) {
if(!e.buttons) return;
const rect = e.target.getBoundingClientRect();
const x = e.clientX - rect.left;
const y = e.clientY - rect.top;
this.draw(x, y);
},
draw: function(mx, my) {
const canvas = document.getElementById('draw_canvas');
const x = mx / canvas.clientWidth * canvas.width;
const y = my / canvas.clientHeight * canvas.height;
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || canvas.width < x || canvas.height < y) return;
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
const r = 40 / 100.0 * (canvas.width / 8); //線の太さ40
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.fillStyle = 'white';
ctx.arc(x, y, r, 0, Math.PI * 2, true);
ctx.fill();
},
getAnswer:function() {
const inputWidth = inputHeight = 8;
const canvas = document.getElementById('draw_canvas')
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
ctx.drawImage(canvas,0,0,inputWidth,inputHeight); //8×8にリサイズ
const img = ctx.getImageData(0,0,inputWidth,inputHeight).data;
//ネガポジ変換
for(let i = 0 ; i < img.length ; i+=4) {
img[i] = 255 - img[i]; //R
img[i+1] = 255 - img[i+1]; //G
img[i+2] = 255 - img[i+2]; //B
img[i+3] = img[i+3]; //A
}
const src = [];
for(let i = 0 ; i < img.length ; i+=4) { //値を格納[255, 255, 0, 0, ...]
src.push(Math.floor((img[i] + img[i+1] + img[i+2]) / 3.0));
}
ctx.fillStyle = 'black';
ctx.fillRect(0,0,inputWidth,inputHeight);
callback = this.update_message;
fetch('http://localhost:5000/numPred', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify(src), //キャンバスの値を識別器に送る
}).then(function(res){
return res.json();
}).then(function(src) {
callback('・・・');
const count = 0;
const countup1 = function() {
if (typeof rnm === 'undefined') { //初回はランダムな数字を生成していないため
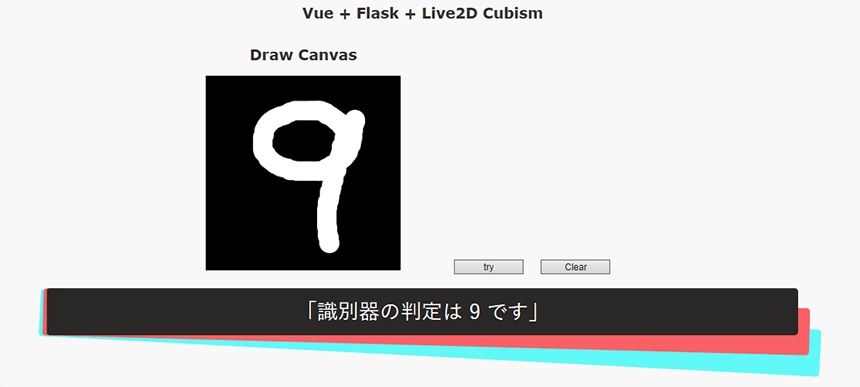
callback('「識別器の判定は ' + src.pred + ' です」');
} else if (rnm == src.pred) {
callback('「一致しました! 識別器の判定は ' + src.pred + ' です」');
} else {
callback('「識別器の判定は ' + src.pred + ' です・・・」');
}
}
setTimeout(countup1, 800);
const countup2 = function() {
const update_num = function(max) {
rnm = Math.floor(Math.random() * Math.floor(max));
return rnm;
}
rnm = update_num(10); //0~9でランダムな数字を生成
callback('// Canvasに数字の '+ rnm +' を書いてください //');
}
setTimeout(countup2, 7000);
}).catch(function(error) {
console.log(error)
})
}}
})
</script>
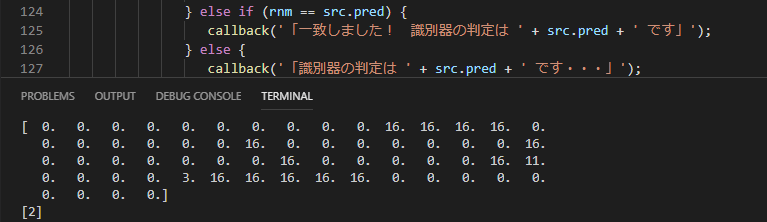
5. 識別器で数字を判定する
1.で作ったpickleファイルで数字の判定を行います。
def predictNum(params):
from sklearn.externals import joblib
forest = joblib.load('./trained-model/digit-clf.pkl')
pred = forest.predict([params])
return pred
Vueから送られてきたキャンバスの値を整えて判定を行います。
@app.route('/numPred', methods = ['GET', 'POST'])
def numPred():
src = request.json
params = np.asarray(src, dtype = float)
params = np.floor(16 -16 * (params / 255))
if request.method == 'POST':
# 上記の判定を行って、結果をVueに返す
pred = predictNum(params)
return make_response(jsonify({
'pred': pred.tolist()
}))
elif request.method == 'GET':
return render_template('numPred.html')
6. CubismWebの画面を表示する
前回記事(アヤメの分類)と同じ手順でCubismWebの画面を設置します。

7. 識別器の判定結果に合わせてCubismWebのモデルを更新する
メッセージウィンドウに出力されるテキストを利用して、条件を分岐させることにしました。
window.onload = () => {
let isCor = false;
let isInc = false;
let isAns = false;
const getbtn = document.getElementById("btn");
getbtn.onclick = () => {
const count = 0;
const countup = () => {
const getmes = document.getElementById("mes");
if (getmes.textContent.indexOf('一致') != -1) { //メッセージに「一致」というテキストがあったら
isCor = true;
} else if (getmes.textContent.indexOf('です・・・') != -1) {
isInc = true;
} else {
isAns = true;
}
this.onUpdate = () => {
//onUpdateの中身と同じ//
if (isCor === true) { //メッセージの内容に応じてモーションを更新する
for (let i = 0; i < this._models.getSize(); i++) {
this._models.at(i).startMotion(LAppDefine.MotionGroupAdd, 1, LAppDefine.PriorityNormal);
}} else if (isInc === true) {
for (let i = 0; i < this._models.getSize(); i++) {
this._models.at(i).startMotion(LAppDefine.MotionGroupAdd, 2, LAppDefine.PriorityNormal);
}} else if (isAns === true) {
for (let i = 0; i < this._models.getSize(); i++) {
this._models.at(i).startMotion(LAppDefine.MotionGroupAdd, 0, LAppDefine.PriorityNormal);
}} else {
return;
}
isCor = false;
isInc = false;
isAns = false;
}
}
setTimeout(countup, 1000); //メッセージが表示されるまで少し時間がかかるので、その分処理を遅らせる
}
}